Deep Learning Basics with Pytorch - Part 1
Part 1 of Deep Learning Basics with Pytorch using JupyterLab
This tutorial series is a hands on beginner guide for pytorch.
Let’s get started. This tutorial series will be comfortable to follow on Unix environment. If you are on Windows make sure to use WSL.
Environment Setup
We are going to need our environment. There are many ways to create environment. But we are going to use Conda.
Install miniconda
Go to the anaconda site and install miniconda.
After you setup and activate miniconda. We are going to install all our libraries in this environment. So that our system won’t be dirty.
Activate environment
Conda is a package manager. Our machine learning tools have first class support in conda. Let’s create a basic environment using conda
1
2
conda create -n basic-env python=3.13 -y
conda activate basic-env
Check where our conda env located.
1
conda env list
Now install Jupyter Notebook inside conda.
1
conda install -c conda-forge notebook -y
conda-forge is community driven channel. notebook just contain basic jupyterlab. install jupyterlab for full package.
If you are on NVIDIA and have CUDA installed.
1
conda install pytorch torchvision torchaudio pytorch-cuda=12.1 -c pytorch -c nvidia
run it.
1
jupyter notebook
Open Browser and browse:
http://localhost:8888/tree
select python3 default kernel. Give any name
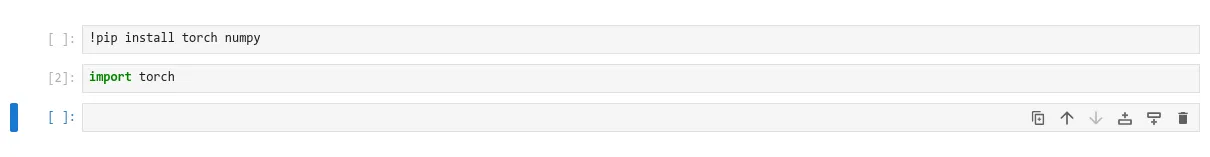
Install pytorch and other libraries.
1
!pip install torch numpy
Next import torch
1
import torch
What is PyTorch and Tensor?
PyTorch is a library for Processing Tensors. A Tensor is a number or a vector or a matrix or a n-dimensional array.
Tensors
Let’s create a basic tensor.
1
2
3
#Number
t1 = torch.tensor(10)
t1
Let’s create different types of tensors
1
2
3
# Vector
t2 = torch.tensor([10, 20, 30, 40])
t2
1
2
3
4
5
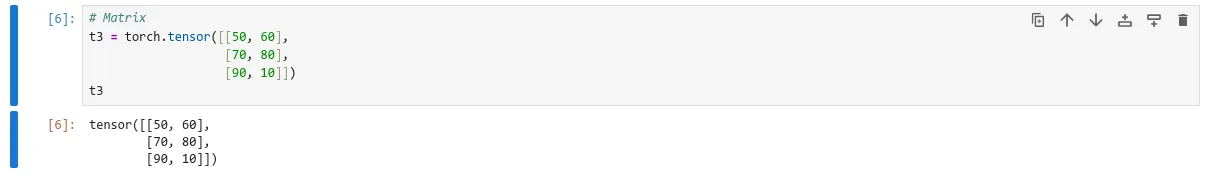
# Matrix
t3 = torch.tensor([[50, 60],
[70, 80],
[90, 10]])
t3
All of these are 1 dimensional array
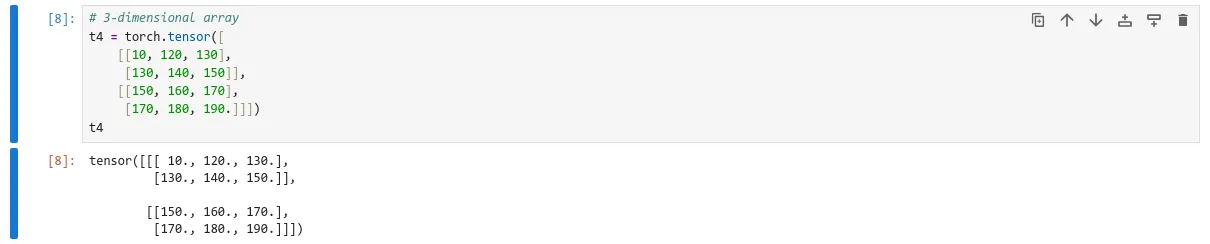
Let’s see 3 dimensional tensor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 3-dimensional array
t4 = torch.tensor([
[[10, 120, 130],
[130, 140, 150]],
[[150, 160, 170],
[170, 180, 190.]]])
t4
Now we can actually see the shape of the tensor
1
2
print(t3)
t3.shape
The output will be torch.Size([3, 2]) Try this on your own
We can also do arithmatic operation with these tensors.
1
2
y = t1 + t2
y
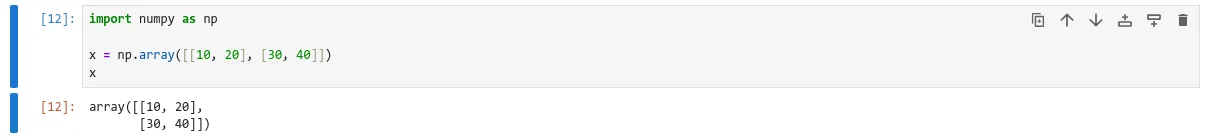
Numpy
Numpy is library for mathmatics and scientific computing in python.
Let’s see how Numpy array looks like
1
2
3
4
import numpy as np
x = np.array([[10, 20], [30, 40]])
x
So, In this tutorial we have just touch the water. We will be continuing this tutorial.